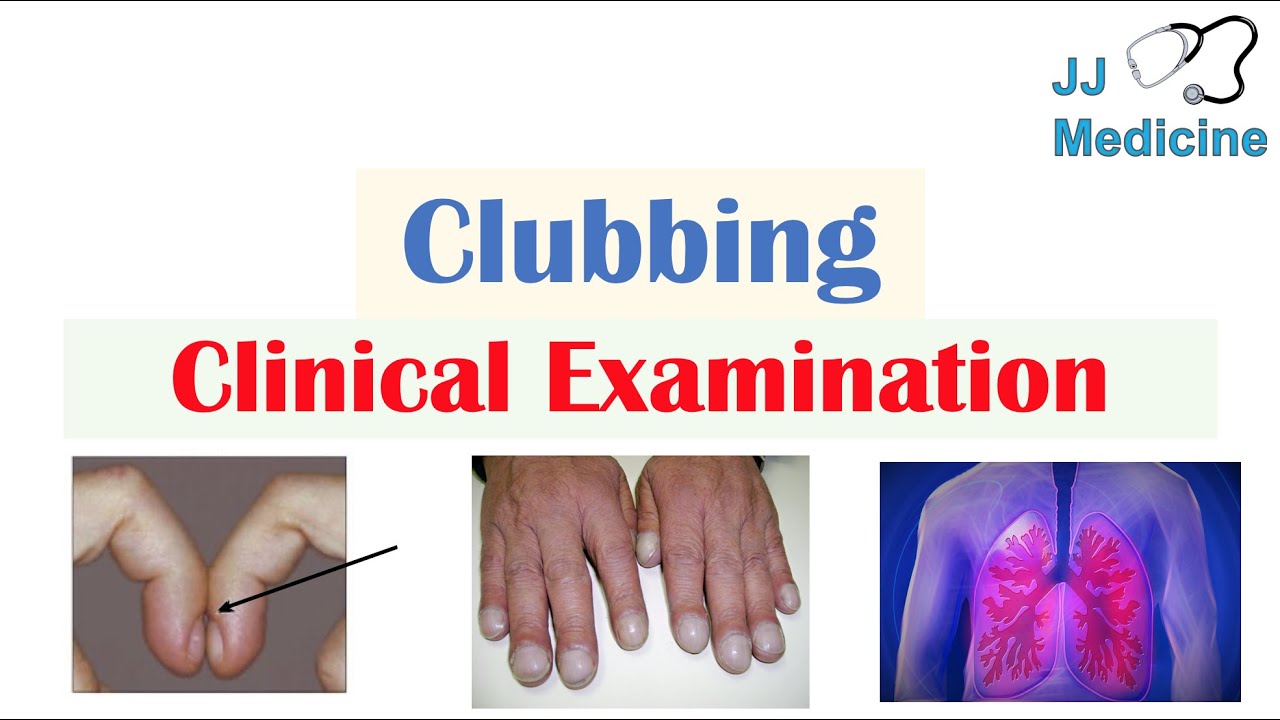
Understanding the Manifestations of this Condition: A Comprehensive Overview of the Presenting Signs and Symptoms
This condition is characterized by a specific set of physical signs and symptoms. These manifestations can vary in severity and presentation depending on the individual and the underlying cause. Common signs may include localized pain, inflammation, and a restricted range of motion in the affected joint. Other potential indicators could be redness, warmth, and swelling around the involved area. Symptoms may also include fatigue or general discomfort. Accurate diagnosis often involves a thorough examination, potentially including imaging techniques to visualize the affected region and to rule out other conditions. The precise nature of the symptoms requires careful consideration of the patient's medical history, the location of the discomfort, and the duration of the symptoms.
The recognition and understanding of these symptoms are crucial for timely intervention and appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and management can lead to improved outcomes and minimize potential long-term complications. By identifying and addressing the underlying causes, effective treatment strategies can alleviate discomfort and restore function. Proper evaluation and treatment of this condition are vital for promoting overall well-being and quality of life. The importance of swift and accurate diagnosis cannot be overstated, as appropriate intervention can prevent further damage and complications.
Moving forward, we will delve deeper into the various diagnostic methods employed, the potential causes and contributing factors of this condition, and the available treatment options for effective management.
Clubitis Syndrome Symptoms
Understanding the various manifestations of clubitis syndrome is critical for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Recognizing the key symptoms allows for appropriate interventions and management strategies.
- Pain
- Inflammation
- Swelling
- Restricted Range
- Redness
- Warmth
These symptoms, often localized to the affected joint, can indicate a range of underlying causes and conditions. Pain, inflammation, and swelling are common responses to injury or irritation. Restricted range of motion often signifies damage or dysfunction within the joint structure. Redness and warmth are indicative of inflammation. The presence of these symptoms warrants prompt medical evaluation to determine the precise cause and initiate appropriate treatment. For example, the combination of swelling and restricted motion may suggest a ligament tear or joint effusion, while chronic pain might indicate osteoarthritis or a persistent inflammatory process. Careful analysis of these symptoms, alongside a detailed medical history, allows clinicians to develop a comprehensive approach to care, potentially preventing further complications and improving overall patient well-being.
1. Pain
Pain is a prominent symptom frequently associated with clubitis syndrome. Its nature and characteristics can provide crucial clues for diagnosis and appropriate management strategies. Understanding the different facets of pain associated with this condition is essential for effective treatment and to distinguish it from other potential causes of joint discomfort.
- Location and Intensity
Pain associated with clubitis syndrome is often localized to the affected joint or surrounding tissues. Variations in intensity, from mild discomfort to severe throbbing pain, can indicate the severity of the underlying condition. For instance, sharp, acute pain may suggest a recent injury, while persistent, dull pain may indicate a more chronic condition like inflammation or degenerative changes. The precise location of pain aids in differentiating potential sources and informs diagnostic procedures.
- Character and Quality
The quality or character of painsuch as aching, throbbing, stabbing, or burningcan provide further insights. Aching pain may suggest a gradual inflammatory process, whereas sharp, stabbing pain may indicate a more acute injury or impingement. Differentiating these characteristics helps to identify the potential etiology of pain and guide treatment planning.
- Aggravating and Alleviating Factors
Understanding factors that exacerbate or alleviate the pain can be informative. Activities like specific movements or positions that increase pain may pinpoint the affected structures or joints. Conversely, activities or therapies that mitigate pain offer clues to potential treatments. For example, rest may alleviate acute pain associated with a recent injury, while certain exercises may help address chronic pain related to joint stiffness.
- Associated Symptoms
Pain in the context of clubitis syndrome is often accompanied by other symptoms, such as swelling, redness, warmth, or limited range of motion. The presence and interplay of these symptoms provide a more complete picture of the condition's severity and guide clinical decision-making. The interplay of pain with other symptoms assists in confirming or refuting the potential diagnosis of clubitis syndrome.
Pain is a multi-faceted symptom that, when considered in conjunction with other physical manifestations and a thorough medical history, contributes significantly to a proper diagnosis and treatment plan for clubitis syndrome. By understanding the location, intensity, quality, aggravating factors, and associated symptoms of the pain, clinicians can better assess the underlying condition and implement appropriate interventions to alleviate discomfort and promote recovery.
2. Inflammation
Inflammation is a crucial component of clubitis syndrome symptoms. It represents a complex biological response to various stimuli, including injury or irritation. In the context of clubitis syndrome, inflammation manifests as redness, warmth, swelling, and pain, directly impacting the affected joint or surrounding tissues. The inflammatory process, while initially protective, can become problematic if prolonged or excessive. This persistent inflammation can lead to further damage and dysfunction within the joint, contributing to the chronic symptoms often observed in clubitis syndrome. Acute inflammation, a rapid response to injury, can be a key indicator of a recent incident, while chronic inflammation may signal underlying conditions contributing to the persistent nature of the syndrome.
The importance of understanding inflammation in clubitis syndrome extends beyond symptom recognition. Inflammation is a significant marker for the severity and potential progression of the condition. The intensity and duration of inflammation directly influence the extent of tissue damage. Careful assessment of inflammatory markers, alongside clinical examination, can aid in differentiating between various forms of joint pain and help refine diagnostic approaches. Monitoring inflammatory responses during treatment allows for adjustments to therapies and provides insights into the effectiveness of interventions, thereby promoting more efficient management strategies. This understanding is crucial for evaluating the long-term health impact and for tailoring interventions to minimize the potential for further complications.
In conclusion, inflammation plays a pivotal role in the presentation and progression of clubitis syndrome symptoms. Recognizing the significance of inflammation, its various presentations, and its impact on the condition allows for a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. Monitoring and managing inflammation effectively are crucial for improving outcomes and reducing the risk of long-term complications associated with this syndrome.
3. Swelling
Swelling, a common manifestation in various medical conditions, plays a significant role in the clinical presentation of clubitis syndrome. Its presence, location, and characteristics offer valuable diagnostic clues. Understanding the different facets of swelling in this context is essential for accurate diagnosis and informed treatment decisions.
- Etiology and Mechanisms
Swelling in clubitis syndrome, like in other musculoskeletal conditions, typically results from increased fluid accumulation in the affected tissues. This fluid accumulation can stem from various underlying processes, including inflammation, trauma, or vascular dysfunction. Understanding the specific mechanisms driving fluid retention is essential for targeting effective treatment strategies. For example, inflammatory swelling is often characterized by warmth and redness alongside the swelling, whereas trauma-induced swelling might present with bruising or other signs of tissue damage.
- Location and Extent
The location and extent of swelling are crucial diagnostic indicators. Localized swelling, confined to a specific joint or area, may suggest an isolated injury or inflammation within that region. Generalized or diffuse swelling, on the other hand, could indicate systemic conditions impacting multiple joints or tissues. Careful assessment of swelling's precise location and its relationship to surrounding structures is vital for distinguishing potential sources and guiding diagnostic investigations.
- Characteristics and Associated Features
The characteristics of swelling, such as consistency (e.g., soft, hard), size, and rate of progression, can provide valuable insights. A rapid onset and significant swelling might suggest an acute injury, while gradual swelling could indicate a chronic inflammatory process. The presence of other symptoms, such as pain, redness, warmth, or limited range of motion, often accompany swelling, aiding in refining the diagnosis and highlighting potential underlying causes.
- Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment
Swelling in clubitis syndrome requires careful consideration in the diagnostic process. Combining swelling characteristics with other clinical findings, such as pain patterns and medical history, can help identify potential causative factors. Appropriate treatment approaches depend on the underlying etiology of the swelling. Addressing the underlying causewhether inflammation, trauma, or another factoris crucial for effective management and reducing the likelihood of long-term complications. For instance, acute swelling may necessitate rest and immobilization, whereas chronic swelling often mandates a more multifaceted approach involving medication, physical therapy, and potentially surgical intervention.
In summary, swelling in the context of clubitis syndrome symptoms is not merely a physical manifestation but a crucial component in the diagnostic process. Careful evaluation of its location, extent, characteristics, and associated features provides essential information for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment, ensuring optimal management and reducing potential long-term issues.
4. Restricted Range
Restricted range of motion is a key symptom frequently associated with clubitis syndrome. The limitations in movement directly reflect the impact of the condition on the affected joint and surrounding tissues. A decreased ability to move the joint through its typical range signifies structural or functional impairment. This restriction might stem from inflammation, pain, or damage to the joint capsule, ligaments, tendons, or muscles. The specific limitations in movement often correspond to the affected anatomical structures. For example, limited flexion in the elbow joint might suggest an issue with the elbow flexor muscles or the joint capsule itself.
The practical significance of understanding restricted range in clubitis syndrome is multifaceted. Accurate assessment of the extent and nature of restricted motion aids in diagnosis. Differentiating between limited motion caused by acute injury, chronic inflammation, or other underlying conditions helps guide appropriate interventions. Furthermore, quantifying the degree of restriction provides a measurable outcome for evaluating treatment efficacy. Tracking the progress of motion restoration over time allows for assessing the effectiveness of interventions, adjustments to treatment strategies, or monitoring potential complications. This objective data plays a crucial role in patient care and management, informing decisions about physical therapy protocols, the need for further diagnostic testing, or potential surgical interventions.
In conclusion, restricted range of motion is a significant component of clubitis syndrome symptoms. Its assessment provides valuable diagnostic and prognostic information. Quantifying and tracking the range of motion is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of treatment and monitoring the progression of the condition. By understanding the interplay between restricted range and the other symptoms of clubitis syndrome, healthcare providers can develop more effective and targeted management strategies, improving patient outcomes and overall quality of life.
5. Redness
Redness, a visible manifestation of inflammation, is a pertinent component of clubitis syndrome symptoms. Its presence, location, and intensity contribute to the clinical picture, offering valuable diagnostic clues and aiding in differentiating the condition from others. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and associated factors enhances diagnostic accuracy and guides treatment strategies.
- Vascular Response to Inflammation
Redness arises primarily from dilation of blood vessels in the affected area. Inflammation triggers the release of chemical mediators that cause these vessels to expand, increasing blood flow to the region. This increased blood flow, in turn, results in the visible redness associated with the condition. This response is part of the body's natural immune system mechanisms, designed to deliver resources to areas experiencing irritation or damage.
- Location and Distribution
The location and distribution patterns of redness can provide insights into the specific area affected by clubitis syndrome. Localized redness, confined to a particular joint or tendon sheath, suggests a localized inflammatory process. Diffuse redness, encompassing a broader area, could indicate a more extensive inflammatory response, potentially related to systemic factors. The pattern of redness is vital in distinguishing the specific cause and guiding diagnostic investigations.
- Intensity and Duration
The intensity and duration of redness are significant indicators of the severity and duration of the underlying inflammatory process. Intense redness and prolonged duration frequently suggest a more pronounced inflammatory response and potentially a greater degree of tissue damage. Conversely, subtle or fleeting redness may point to less severe or transient inflammatory triggers. The intensity and duration are important parameters alongside other findings when evaluating the overall picture of the condition.
- Correlation with Other Symptoms
The presence of redness is often accompanied by other symptoms, such as pain, swelling, and warmth. The simultaneous occurrence and interplay of these symptoms provide a comprehensive clinical picture. Analyzing these symptoms in conjunction with the characteristics of redness allows for a more accurate assessment and facilitates the formulation of an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan. This holistic approach is essential to determining the underlying cause and effectively managing the condition.
In conclusion, redness in the context of clubitis syndrome symptoms is not an isolated finding. Its relationship to other clinical presentationsincluding location, intensity, and durationis significant for accurate diagnosis. The interplay between redness and other symptoms provides a more complete clinical picture, aiding in formulating effective treatment strategies. Careful assessment of redness contributes significantly to a comprehensive understanding of the condition and its effective management.
6. Warmth
Warmth, a frequently observed symptom alongside other manifestations in clubitis syndrome, arises from an underlying inflammatory process. Its presence, alongside other physical indicators, helps to delineate the condition and its possible severity. The localized warmth is a physiological response to increased blood flow to the affected area, a key characteristic of inflammation.
- Vascular Response to Inflammation
The increase in blood flow to the affected area, responsible for warmth, is a direct consequence of the inflammatory response. This heightened blood flow delivers immune cells and necessary nutrients to the site, but the dilation of blood vessels can lead to an observable increase in temperature. In the context of clubitis syndrome, this local vasodilation often coincides with other inflammatory markers like redness and swelling, further corroborating the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Severity and Duration of Inflammation
The intensity and duration of warmth can offer clues about the severity and persistence of the underlying inflammation. A localized area of significant warmth, especially in combination with pain and swelling, often signifies a more acute inflammatory response. Conversely, less intense or intermittent warmth might suggest a less aggressive or more chronic inflammatory state. This observation is crucial in differentiating various forms of joint pain or discomfort.
- Differentiating from Other Conditions
While warmth is a common companion to clubitis syndrome, its presence alone cannot definitively confirm the diagnosis. Warmth can also be a symptom of other conditions, including infections, trauma, or even variations in the environment. Careful consideration of accompanying symptoms, such as pain, swelling, and range of motion limitations, alongside a detailed patient history, is essential in differentiating clubitis syndrome from these other possibilities.
- Clinical Significance in Diagnosis
Clinicians utilize warmth as a clinical sign alongside other symptoms in the assessment of clubitis syndrome. Its observation in conjunction with localized pain, redness, and restricted movement strengthens the likelihood of the diagnosis. This integrated approach to symptom evaluation guides subsequent diagnostic investigations and treatment strategies. By interpreting warmth within a comprehensive clinical framework, clinicians can formulate more accurate diagnoses and implement targeted therapies.
The presence of warmth in clubitis syndrome symptoms is a reliable indicator of the inflammatory process underlying the condition. Its intensity and duration provide important information about the potential severity and chronicity of the inflammation. However, it's essential to consider warmth alongside other physical signs and symptoms, as well as a thorough patient history, to arrive at an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions about Clubitis Syndrome Symptoms
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the various symptoms associated with clubitis syndrome. Accurate understanding of these symptoms is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Question 1: What are the most common symptoms of clubitis syndrome?
Clubitis syndrome is characterized by a constellation of symptoms, often including localized pain, inflammation, and restricted range of motion in the affected joint. Redness, warmth, and swelling around the involved area are also possible. The severity and presentation of these symptoms can vary significantly depending on the individual and the underlying cause.
Question 2: How can I differentiate clubitis syndrome from other conditions with similar symptoms?
Distinguishing clubitis syndrome from conditions with overlapping symptoms requires a comprehensive clinical assessment. This includes a thorough medical history, physical examination, and potentially diagnostic imaging studies. Comparison of specific symptoms, location, and duration of symptoms, and consideration of associated factors aid in proper differentiation.
Question 3: What are the potential causes of clubitis syndrome symptoms?
The precise causes of clubitis syndrome remain multifaceted and are not fully understood. Potential contributing factors may include overuse, repetitive strain, trauma, inflammatory processes, or underlying systemic conditions. A careful evaluation of each individual's case history is crucial to identifying possible contributing factors.
Question 4: How are symptoms of clubitis syndrome typically diagnosed?
Diagnosis often involves a multi-faceted approach. This might include evaluating the patient's medical history, physical examination, and imaging techniques (such as X-rays or MRI scans) to visualize the affected area. Laboratory tests, such as inflammatory markers, may also be necessary to assess the severity of the condition.
Question 5: What treatment options are available for clubitis syndrome?
Treatment approaches for clubitis syndrome are tailored to the individual and the specific cause of the symptoms. These strategies can range from conservative measures, such as rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications, to more advanced interventions like corticosteroid injections or surgical procedures. The efficacy of specific treatments can vary widely and necessitates careful consideration by healthcare professionals.
Accurate identification and understanding of clubitis syndrome symptoms are essential for appropriate management and positive patient outcomes. Seeking professional medical advice is crucial for the effective diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
This concludes the FAQ section. The following section will delve deeper into the diagnostic processes and treatment protocols for clubitis syndrome.
Conclusion
Clubitis syndrome presents a complex interplay of symptoms, impacting the affected joint and surrounding tissues. Key manifestations include localized pain, inflammation, swelling, and restricted range of motion. Redness and warmth are frequently observed, all indicative of an underlying inflammatory process. Understanding the nuanced presentations of these symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. Precise characterization of pain, including location, intensity, and exacerbating factors, is essential. Similarly, the extent and nature of swelling, along with associated characteristics like consistency and rate of progression, provide valuable diagnostic information. The limitations in range of motion, often coupled with redness and warmth, suggest structural or functional impairment. Careful consideration of these interconnected symptoms is vital in differentiating clubitis syndrome from other conditions with overlapping presentations. Accurate diagnosis relies on a comprehensive evaluation encompassing clinical examination, patient history, and potentially diagnostic imaging techniques. This comprehensive approach facilitates the development of individualized treatment strategies, aimed at managing symptoms and improving overall patient outcomes.
The significance of recognizing and understanding clubitis syndrome symptoms cannot be overstated. Early and accurate diagnosis facilitates timely intervention, potentially minimizing the risk of long-term complications. Further research into the underlying mechanisms driving the symptom presentation is essential for refining diagnostic criteria and developing more effective therapeutic approaches. Clinicians are encouraged to remain vigilant in their evaluation of patients presenting with these symptoms, focusing on the nuances of each case to provide optimal care and promote patient well-being. The ongoing study of this condition will undoubtedly yield a deeper understanding of its complexities and contribute to better patient outcomes in the future.
Article Recommendations
- Mellstroy Net Worth 2024
- Shyna Khatri Web Series Phenomenon A Sensational Journey
- Is Keanu Reeves Sick